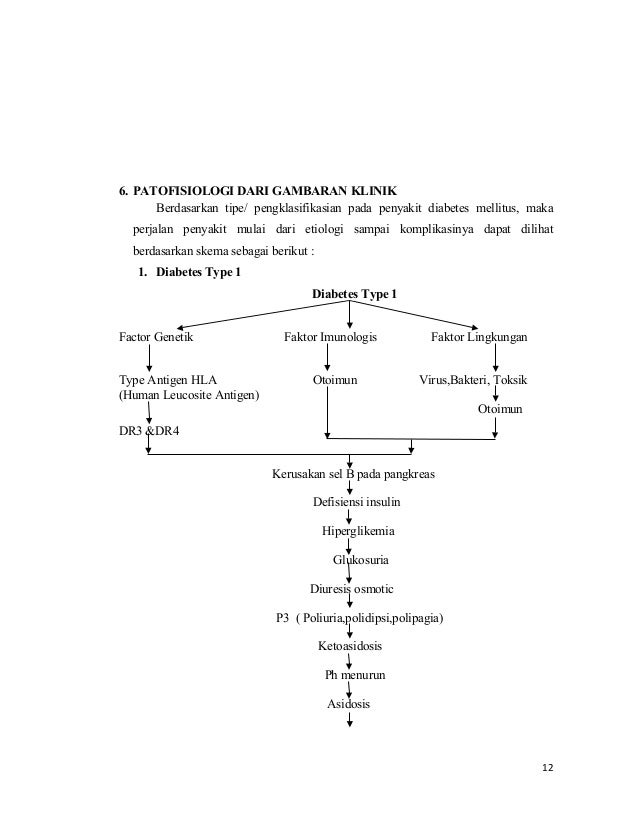
6. Diabetes Mellitus
Some people with prediabetes may have some of the symptoms of diabetes or even problems from diabetes already. you usually find out that you have prediabetes when being tested for diabetes. if you have prediabetes, you should be checked for type 2 diabetes every one to two years. results indicating prediabetes are: an a1c of 5. 7%–6. 4%. Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented. you can decrease your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. if a close relative—particularly, a parent or sibling—has type 2 diabetes, or if your blood glucose test shows \\"pre-diabetes\\" (defined as blood glucose levels between 100 and 125 mg/dl), you are at increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes. you can help to prevent type 2 diabetes by 1. maintaining your ideal body weight. 2. exercising regularly—such as a brisk walk of 1-2 miles in 30 minutes—at le Carl bianco m. d. provides a 6-part graphical in-depth look at heart disease, heart attacks and angina. topics include atherosclerosis, hypertension, cholesterol, smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus and stress.
Diabetes Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
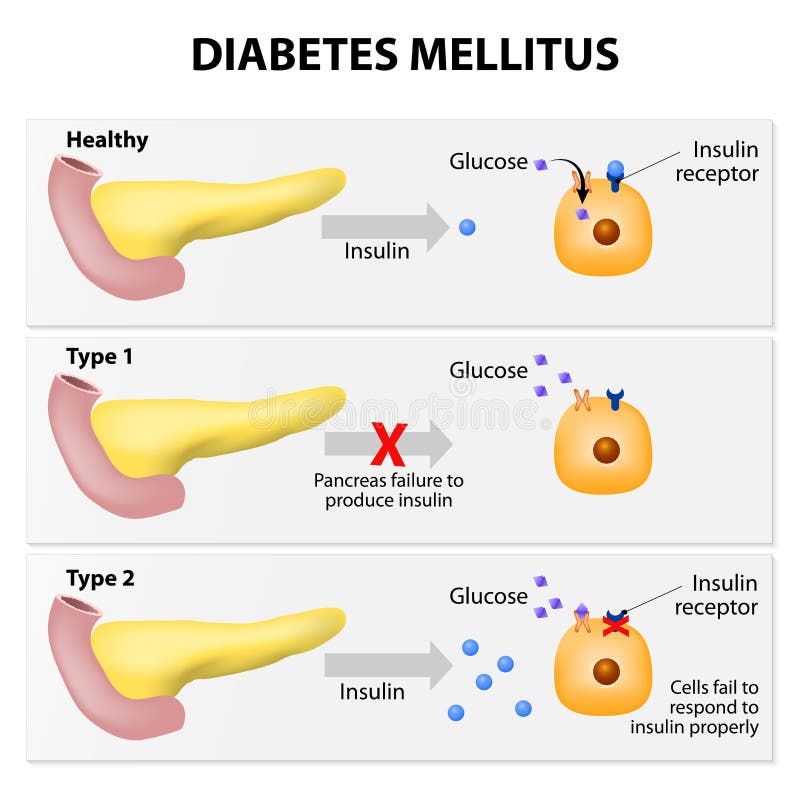
Diabetes mellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. See full list on mayoclinic. org. Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease caused by the failure of pancreatic organs to adequately produce the hormone insulin, causing an increase in glucose levels in the blood. dm is one of the non-communicable diseases and is one of the important public health problems. the incidence of diabetes mellitus has increased in decades. See full list on mayoclinic. org.
Diabetes Insipidus Vs Mellitus Differences Symptoms
Diabetesmellituspart 6 Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetesmellitus (dm), commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level over a prolonged period of time. symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst, and increased appetite. if left untreated, diabetes can cause many complications. acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or. Diabetesmellitus signs and symptoms if you think that you have diabetes, visit your doctor immediately for a definite diagnosis. common symptoms include the following: about 50 percent of people with 6. diabetes mellitus type 2 diabetes don't experience any symptoms and don't know they have the disease. Diabetesmellitus and diabetes insipidus share the first word of their name and some of the same symptoms. but that’s where the similarities end. these two diseases aren’t related. they cause. The action of il-6 in type 1 diabetes pathogenesis may in principle be exerted at the level of the target β-cell, and/or at immune regulation, and/or at the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. several investigations of the putative impact of il-6 on type 1 diabetes have been reported (8,31–42).
What is diabetes mellitus: definition, 6 risk factors, and diagnosis / what is diabetes mellitus? diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease caused by the failure of pancreatic organs to adequately produce the hormone insulin, causing an increase in glucose levels in the blood. dm is one of the non-communicable diseases and is one of the important. Interleukin-6 (il-6) is a proinflammatory cytokine that decisively induces the development of insulin resistance and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (t2dm) through the generation of inflammation by controlling differentiation, migration, proliferation, and cell apoptosis.
4) peak flow meter (7) copd (13) depression (6) diabetes mellitus type i (5) diabetes mellitus type ii (12) 6. diabetes mellitus 4) peak flow meter (7) copd (13) depression (6) diabetes mellitus type i (5) diabetes mellitus type ii (12) Diabetes is diagnosed by testing the blood for sugar levels. blood is tested in the morning after you have fasted overnight. typically, the body keeps blood sugar levels between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl), even after fasting. if a blood sugar level after fasting is greater than 125 mg/dl, diabetes is diagnosed. your doctor will examine you to look for: 1. obesity, especially abdominal obesity—a condition that greatly raises a person's risk for type 2 diabetes. 2. high blood pr
Diabetesmellitus is a condition defined by persistently high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. there are several types of diabetes. the two most common are called type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. during digestion, food is broken down into its basic components. carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, primarily glucose. Diabetes types. diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a metabolic disease that causes high blood sugar. the hormone insulin moves sugar from the blood into your cells to be stored or.
Diabetes mellitus is a condition defined by persistently high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood. there are several types of diabetes. the two most common are called type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. during digestion, food is broken down into its basic components. carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, primarily glucose. glucose is a critically important source of energy for the body's cells. to provide energy to the cells, glucose needs to leave the bloodstream and get insid Diabetesmellitus, also known simply as diabetes, involves how your body turns food into energy. learn more about the different types of diabetesmellitus.
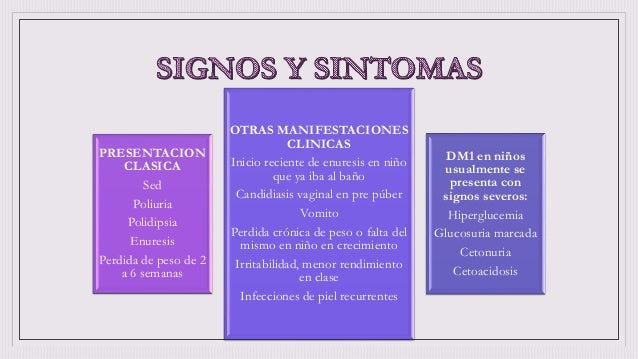
See full list on drugs. com. Diabetes initially might not cause any symptoms. it can sometimes be caught early with a routine blood test before a person develops symptoms. when diabetes does cause symptoms, they may include: 1. excessive urination 2. excessive thirst, leading to drinking a lot of fluid 3. weight loss. people with diabetes also have an increased susceptibility to infections, especially yeast (candida) infections. when the amount of insulin in the blood stream is too low, extremely high blood sugar levels c

Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong illness. usually, type 2 diabetes is also life-long. however, people with type 2 diabetes can sometimes 6. diabetes mellitus restore their blood sugar levels to normal just by eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and losing weight. gestational diabetes usually goes away after childbirth. however, women with gestational diabetes are at high risk for developing type 2 diabetes later in life. in people with diabetes, aging and episodic illnesses can cause the body's insulin resist See more videos for 6. diabetes mellitus.
Comments
Post a Comment